Optimizing Website Content (Blog Posts, Product Pages & More)


Join our newsletter
Get access to trusted SEO education from the industry's best and brightest.
There are different strategies to optimize website content, depending on the type of content you’re working with. You may want to optimize blog posts and other long-form content, like case studies, to rank your website for industry-related keywords. Or, you may be interested in optimizing your homepage or product pages for category-specific or product keywords.
But the steps between processes are not hugely different, and once you understand the key ideas and goals of optimizing content, you’ll be able to easily produce top-ranking content across your site.
Not to mention, content optimization software proves hugely beneficial here (regardless of the content you’re working with).
These solutions show writers how to follow on-page SEO strategies and create optimized blog posts and landing pages, hence the name. They deliver keyword reports with SERP analysis tools, details on search intent, and suggested headings and terms to use in content — so you can determine positioning, structure outlines, and write optimized content.
We put together this guide to cover:
The steps to optimize long-form website content
Best practices to optimize homepages and product pages
Reviews of the top content optimization software
FAQs about optimizing website content
Clearscope covers everything writers need to learn content optimization strategies. Our platform lets you research target keywords, compare page-one results, and create unique content (that outranks competitors). And it’s highly intuitive, so any writer can learn the ropes.
Explore our platform here or schedule a free demo with our team to talk custom solutions.
Optimizing website content like blog posts & case studies
In this section, we’ll run through the most important considerations when optimizing long-form content.
We’ve also written in-depth guides on this topic — which we’ll link to below — so if you want more details on any of the steps, click over to those.
1. Target a specific keyword
First, each piece of content should be assigned a target keyword (aka the query you want to rank for in search engines).
You may target a single keyword or hit on multiple keywords in one piece of content.
Note: Even if you don’t strategically target secondary keywords, you’re still likely to rank for related search queries.
If you haven’t already read up on keyword research and assigning topics, you can do so here:
Keyword Mapping: What It Is and How to Map to Your Purchase Journey (+ Template)
Topic Clusters: What Are They? Do They Help Your SEO? (with Video)
Then, you should perform SERP research to learn more about search intent and what Google ranks for the target keyword. Open up the first page of search results and pay attention to:
The sites Google ranks.
The type of content they produce — the content format, the sections/details they include.
Information in SERP features, like featured snippets, questions in “People Also Ask?” and recommended brands or products.
Related searches.
The information you gather here can help you understand the goal of the searcher and develop your content angle.
Pro tip: Content optimization software like Clearscope can streamline topic research by pulling these takeaways for you. Our keyword discovery lets you open and view the SERP quickly, and reports provide big-picture insights so you can see themes and questions from SERP features, compare competitor outlines, and view a list of related terms.
2. Tailor content to appeal to search intent
It’s extremely important to remember that your #1 audience is always the person doing the search (yes, even when writing SEO content). Google prioritizes high-quality content that satisfies readers’ goals above all else.
So, of course, you still want to take steps to optimize content for search engines, but if you keep in mind that Google’s primary goal is to deliver helpful content for the searcher, it’s easier to focus on content quality.
As you review SERP results and build out your strategy for content, it’s essential to ground yourself in the reader’s shoes and consider what would be most valuable to them.
For example, if you target a “how to” query like “how to track search engine rankings,” you’ll need to create a blog post that covers a list of steps and software to use.
At this step, you should determine:
The questions to answer in content.
What searchers aim to accomplish — and how to help them achieve those goals in the best way possible.
The topics to cover and solutions to recommend.
The outline structure. (Note: Follow the recommended heading format when outlining content. Use one H1 for the title, H2s for main sections, and H3s for subheadings.)
Read more: Your Guide to Analyzing User Intent for Better SEO Results
3. Write optimized content with the help of SEO reports
Here’s where you can use content optimization software to create SEO-friendly blog posts and landing pages. As mentioned, content reports contain SERP takeaways and guidelines for writing, so you can determine:
What’s important to talk about in content (themes to cover, questions to answer).
How to structure content and move between topics.
The details to include in each section.
These reports supplement existing workflows so writers can follow SEO suggestions as they outline, draft, and edit; creating optimized content doesn’t require you to reinvent the wheel, you just need to tweak processes so you can cater to both searchers and search engines.
Here’s an example of a Clearscope SEO report:
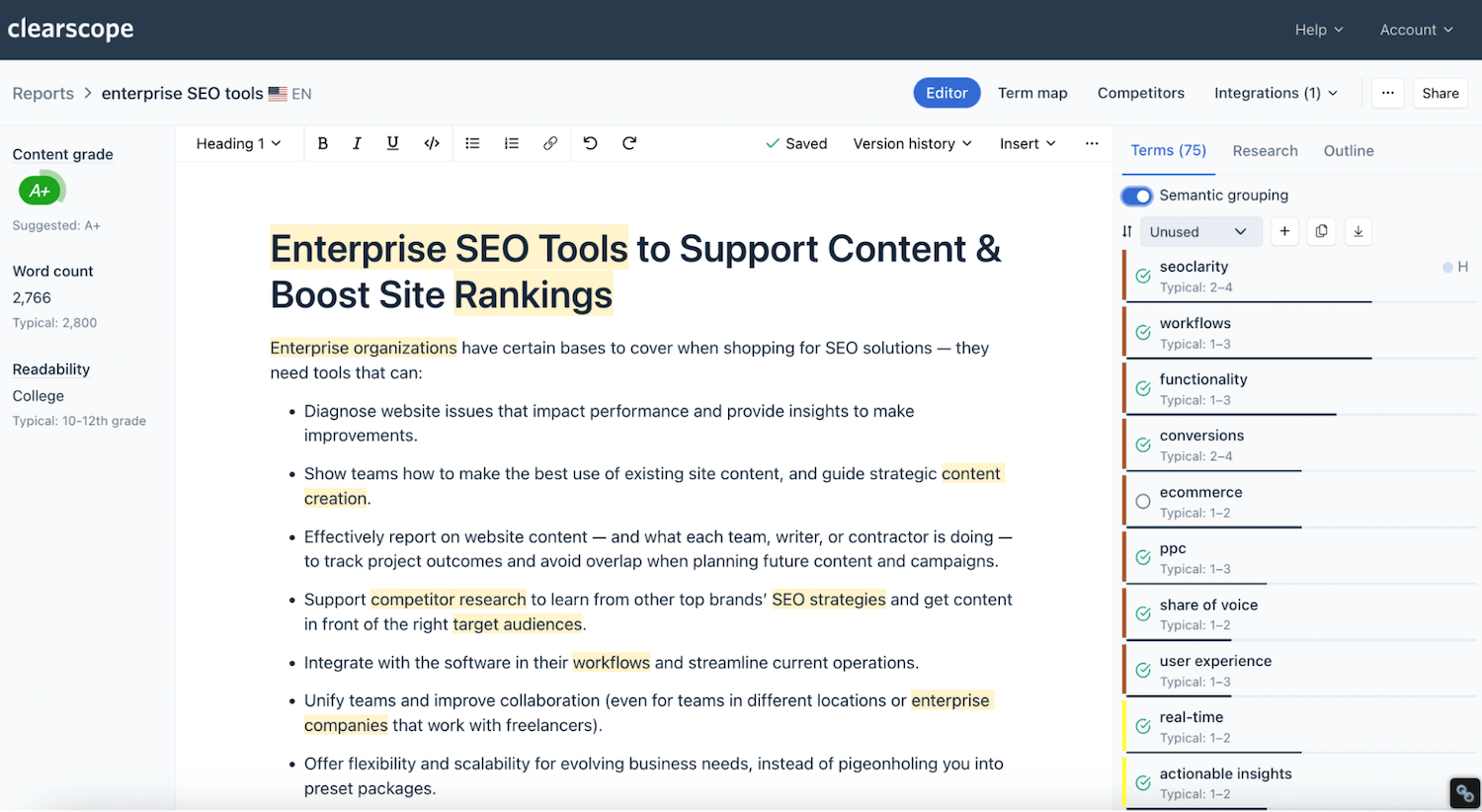
In it, you can see:
A list of terms to include in content — headings are marked with an “H,” the semantic grouping feature filters like terms so you can flow from topic to topic naturally, and you can sort the list by “Unused” terms to see what’s leftover. We check terms off as you go and display real-time SEO grades so you know when content is fully optimized.
The “Research” tab — this includes themes from the SERP, questions to answer, and common citations to link in content.
The “Outline” tab — this is where you can compare competitor outlines and see each page’s SEO score and rank (on desktop and mobile).
Metrics like SEO score, word count, and readability level so you can track progress as you work.
Highlights in content — we highlight the terms from our list so you can make edits without removing suggestions.
Then you can naturally write high-quality content while checking the boxes to optimize for search engines. You’re not keyword stuffing or worrying about dropping exact terms in specific places. We take the guesswork out of SEO with clear recommendations to rank content on page one.
Remember, your main priority is to create content that is genuinely interesting and helpful to readers — it should provide searchers the information they’re looking for, answer their questions, offer recommendations, and give readers resources to take the next steps towards their goals.
High-quality content that’s tailored to the reader will always perform better than content that’s written around SEO rules.
You can read more about this step here: SEO Writing: 5 Steps & Tools to Create Top-Ranking Content
4. Add internal and external links in content
Content requires links — both internal links (to other pages on your site) and external links (to other credible sites) — to perform well in search engines.
Here are a few rules for links:
They should be relevant and helpful to the reader. Don’t drop in links without reason.
Use descriptive anchor text, with relevant keywords, so anchors tell readers where links direct them.
Only link to other sites with high DA ratings — you can check these scores with an SEO tool like Ahrefs — so search engines see you’re citing authoritative and reliable sources.
Include at least one external link.
Include several (a dozen or so, if not more) links to other pages on your site. Linking to high-ranking pages can also be a smart strategy.
Read more: 5 Effective Internal Linking Strategies to Improve Your SEO
It’s worth noting that low bounce rates show Google that your content provides the details and resources users need to continue their journey from your page (meaning that readers actually engage with your content). Better engagement metrics = better rankings.
5. Add call to actions (to optimize content for conversions)
You can drive conversions from content by dropping call to actions that direct readers to complete specific goals (e.g., make a purchase, complete a contact form, request a demo).
We normally suggest placing these at the start and end of content — at the bottom of the introduction and after the last section — but you can also drop them throughout the page, where it feels natural.
For example, if you were writing a product comparison guide and wanted to promote sign-ups for one product vs. another, you could include a CTA within that particular product section so it’s easy for readers to take next steps with what you’re promoting.
When writing CTAs:
Use clear and concise phrasing, and keep call outs short (1–3 sentences).
Think about the search intent of the target audience — what’s most relevant and valuable to them — and write something unique to their goals.
Write persuasively but without sounding “salesy.”
6. Use images, videos, infographics, and other supporting media in content
Place media within content to illustrate important points, support text, and improve readability. Readers prefer blog posts, guides, and stories that have visuals to break up content, and as such, Google is more likely to rank content with media over content without.
Include media where it supports content: include pictures of products in review guides, images or videos in how-to guides, or graphs to visualize data — don’t add generic media or stock imagery just to “fluff up” content.
Then, include alt-text with in-line media: this works as a placeholder when content doesn’t load correctly or users access content with assistive reading devices. However, this also helps SEO because it gives crawlers extra context about what media contains, and you can plug relevant keywords in alt-text.
7. Optimize content for readability
After editing your post, take another pass to improve scannability — some refer to this as “optimizing content quality.”
The goal here is to make content easily readable and engaging:
Use clear phrasing in headings.
Avoid overly-long sentences.
Break up walls of copy.
Add lists and bullet points.
Use bolding and italics.
Add a table of contents if content is lengthy — that way, readers can skip to what they’re interested in.
Include FAQs to directly answer specific questions or cover related points.
Content should be somewhat skimmable so that readers can scan through, find what they’re interested in, and gather the important points.
Pro tip: Formatting content so it’s easily scannable improves your likelihood of appearing as a SERP feature. For example, if somebody searches “how to clean a mattress,” and your content contains a concise list of (accurate) steps, Google may show your list at the top of search results.
8. Add the SEO title tag & meta description (with keywords)
In addition to the page title, you also need to write an SEO title and meta description for your website content. In many cases, you can re-use the page title as the SEO title, you just want to make sure it meets a few requirements:
Titles should contain target keywords.
They should clearly indicate what content covers.
They should be more competitive, catchy, and attention-grabbing than what you already see in the SERP.
They should be shorter than 580 pixels — you can check title and meta lengths here.
Meta descriptions should also include target keywords, describe page content, and meet specific length requirements.
A good rule of thumb: Take another look at the SERP and think of ways to stand out.
Do you notice commonalities amongst titles?
Which posts, based on title alone, seem most helpful to readers?
What can you say that would be more appealing to searchers?
If your title persuades readers to click in, search engines will see that your content is relevant to searchers (and that users choose your content over other pages). A high click through rate shows Google that you have the best content for the given query — and this could push you to the top positions in organic search results.
The caveat here is that your content also needs to keep readers on the page once they visit — which is why content quality and the steps above are so important. If readers leave after a few seconds, Google will see content doesn’t deliver on expectations, and you could lose those page-one positions.
You can read more about creating SEO-friendly blog content in our guides:
Optimizing homepages & product pages
A lot of the steps above also apply here, but obviously, the best practices are a little different because landing pages have unique elements and shorter quips of copy (copywriting vs. blog writing).
In the case of landing pages, you still need to:
Target a specific keyword — again (for our more advanced readers), you may choose to target multiple keywords with one page; just be sure keywords strongly relate and you see overlap in SERP results.
Perform SERP research — take note of the other brands on page one, compare page titles, and check out competitor sites. What catches your eye?
Compare competitor content — what information, features, or benefits do they highlight? What page elements do you notice (e.g., FAQs, reviews, social widgets)? What are the strengths and weaknesses of content?
Identify search intent and focus on the details most important to the reader. Many teams get caught up in what they want to say or sell without thinking about how to best position copy for the audience's pain points.
Write SEO-friendly content that’s tailored to the readers’ goals.
Add images and links.
Include strong SEO titles and meta descriptions that include target keywords.
Now let’s cover the considerations for landing pages.
When working on product or feature pages, you need:
Descriptive but simple product names. Try to use the generic product name (product keyword) with any branded copy — for example: [Brand Name] Cotton Tee — so you’re more likely to be found when somebody searches the product category.
Unique product descriptions that include the target keyword — these don’t need to be overly elaborate or “cutesy,” you want to write persuasively, but you can make these short and straightforward. Include anything that’s relevant to the shopper or purchasing decision.
To include complete product names in URLs.
A variety of high-quality media (e.g., images, videos, 3D models) to display your product or service.
Optimized media with alt tags — more on that below.
Sections with important information for shoppers; product pages should always include “Product Details,” reviews, and FAQs to answer questions about purchasing, use, maintenance, etc. Or, in the case where you’re creating a booking page for a hotel or event, you’d want to include details about how to check-in or where to park, for example.
Note: Reviews are not only helpful for the customer experience, but they can help SEO, too. Products that receive a high number of reviews and good user feedback are more likely to be shown in the Google Shopping bar. You can gather and post reviews on your site, or feed them directly from Google (or another review site) via widget.
Check out our post with strategies to earn more online reviews.
Speaking of appearing in SERP features, adding structured data to your site (“Product,” “Reviews,” or “Rating” schema) also helps search engine algorithms recommend you in related queries.
You can add schema to your site code and control what appears below page URLs in the SERPs. For example, “FAQ” schema will show FAQs from your landing page, “Reviews” will display product reviews.
Then, you can also improve landing page SEO by optimizing UX. Specifically, fine-tune desktop and mobile usability, boost page speeds, remove pop-up ads (or anything that could block users from engaging with your page), check that buttons and menus are clear and functioning, and run a technical audit.
You can use an SEO tool like Google Search Console to diagnose back-end issues and follow recommendations to improve site performance and user experience. However, you can also hire UX agencies to tweak your site design and run A/B tests to increase engagement times and conversions.
Pro tip: Many teams don’t see content optimization software as an applicable tool to write product or landing pages. And while this may be true in some cases, Clearscope reports are designed to work for all types of content creation.
We’re careful to list unique terms and headings in reports, and lists are relatively short, so you can weave recommendations in while copywriting. These recommendations also show you what to include in the “extra details” as they emphasize what others talk about and readers want to know. You can use recommendations to fill in product details or gather ideas for FAQs.
Read more: 5 SEO Writing Assistants to Support Content Creation
Best content optimization software to guide SEO writing
Now, let’s talk more about using content optimization software (and three of the most popular solutions) to write blog posts and web pages.
Clearscope: Create unique, SEO-friendly content without guesswork

Clearscope supports each stage of content development. Our platform includes:
Keyword Discovery to research topic ideas and build a strong content plan.
Content Briefs, so managers can assign topics and share the details and expectations for content.
SEO Reports to streamline SERP research and show writers what’s important to optimize content and achieve top rankings.
Clearscope Content Inventory to track real-time SEO scores for published web pages (blog posts, product pages, any “SEO content”) and plan updates.
What differentiates Clearscope from other platforms is ease of use: the dashboard and features are intuitive, and our reports don’t require prior SEO knowledge to decipher. Everything is plainly laid out for you, so you can work through each step of content creation and check recommended boxes efficiently.
Our solution supports natural, high-quality writing with concise terms lists and natural language processing to understand multiple variations of suggested terms; the emphasis is never on squeezing in keywords or “optimizing content.” Writing and optimization become a seamless process.
This also differs from some of the other content optimization tools (especially with the rising interest in AI). Many tools go overboard with recommendations — we’ve heard Surfer reports contain literally hundreds of list items — or put too much focus on automating processes. Just plug in the keyword and AI will write it for you!
We aim to strike that middle ground where Clearscope can build upon and improve your current processes — you can quickly and more productively write top-ranking, unique content that drives results.
We offer plans for teams and individuals; you can explore our platform here or contact us for a free demo.
Read more: What Is Clearscope? Software to End SEO Guesswork
MarketMuse

MarketMuse is a common choice for content marketing teams that need a little more help with keyword research and constructing content plans.
The platform includes SEO reports to support content writing, but most choose this solution for its content strategy tools. It lets you search keyword ideas, analyze the search terms competitors rank for, build content clusters, and plan out topics.
While MarketMuse has strong keyword research tools, some note complaints with content reports. You have to run multiple reports per keyword — takeaways from SERP results and competitor content are available in one report, recommendations for content writing are included in another — so you run out of report credits quickly. Not to mention, reports can be difficult to understand if you’re a brand-new SEO.
Read more: Best MarketMuse Alternatives: Clearscope + 3 Runners Up
Surfer SEO

Surfer is an SEO strategy solution for teams that need help improving site performance, identifying keyword opportunities, and creating new content.
Like Clearscope and MarketMuse, they have features to build content plans and reports to write SEO content. However, most teams choose Surfer for its “Grow Flow” dashboard. Which is arguably the strongest feature, as users commonly note issues with the other tools.
(For example, Surfer isn’t a good option for teams creating landing pages because reports recommend hundreds of terms to achieve “optimized content” — which also means it’s not super user-friendly for blog writing, either.)
The Grow Flow dashboard monitors your site and performance in search engine results pages and sends ten personalized SEO recommendations each week. These can be as simple as, “add a link in X post,” or require more comprehensive or technical changes. Surfer can tell you when content requires updates, rankings decline, or links break; it can also suggest new keywords for your content plan.
The biggest issue with Grow Flow is that you have no control over the types of recommendations Surfer sends. There could be weeks where reports don’t contain anything valuable, and other weeks where Surfer recommendations are more helpful.
Some also say that it’s hard to understand what’s important from reports (especially if you have no prior SEO background). Recommendations may be so simple that they’re not worth the time or attention.
Read more: Best Surfer SEO Alternatives: Clearscope + 3 Runners Up
FAQs about website content optimization
How do you optimize media like images and videos?
Here are the steps to optimize website media:
Compress images and videos so they load quickly — some editors have a “save for the web” function, or you can use a file compression tool.
Embed large video files to maintain quality while streaming.
Update the file name (before uploading to your CMS) so it’s descriptive and includes the target keyword — this metadata is helpful to crawlers!
Add titles and alt-text with media during upload.
Include image tags and descriptions with videos so users can see these previews when they hover on content.
Add images and metadata to your site map.
Include structured data for media so it can appear in search engines.
Double-check your site is mobile responsive so media loads and appears correctly.
How do you optimize for backlinks?
The short answer? Write content that’s link worthy. Viral content or content with fresh insights, unique advice, controversial opinions, or new discoveries is naturally going to receive links because it sparks reader interest.
One way to gain backlinks is to publish studies about recent research or survey findings, as writers always want to reference the most current facts.
But if you want to put all content in a good position to receive backlinks: focus on originality. Say something new. Drop insights from your experiences. Fresh content vs. content that parrots competitors is more likely to earn backlinks.
You can also create link building relationships with other sites — you can reach out the old-fashioned way or use an agency to establish these connections.
Read more: How to Get Good Backlinks: A Step-by-Step Guide
How can you optimize website performance?
Perform a technical SEO audit to identify back-end issues like confusing URL structures, non-indexed pages, broken links, and expired redirects. You should also dig into desktop and mobile usability, and address any issues that slow page load times.
You can use Google Search Console to view core web vitals and resolve many of the issues that hurt site performance, but you may want to run a more in-depth audit (with a tool like Screaming Frog) if you don’t notice improvements after implementing changes from GSC.
You can think of “optimizing website performance” as the maintenance to keep your site and web pages operating smoothly and visible to search engines.
Clearscope reports simplify SEO writing so you can create optimized website content with ease. Whether you’re building out your blog or creating content for landing pages, our guides show what’s relevant to searchers while providing recommendations to hit the first page of search results.
Get started in our platform to explore our SEO tools and begin writing optimized content. You can also schedule a free demo to learn more and talk about custom packages.



